
Reblogged on WordPress.com
Source: “It is no measure of health to be well adjusted to a profoundly sick society.” ― Jiddu Krishnamurti


Reblogged on WordPress.com
Source: “It is no measure of health to be well adjusted to a profoundly sick society.” ― Jiddu Krishnamurti
Please donate so I can keep the fight going! Running on fumes!

Need allies and funding to continue the fight against institutional injustice in the medical profession and work towards physician (professional ) health reform.
Please help me work toward real change on disruptedphysician.com before it is too late.
To make a contribution please click here or visit gofundme website.

BOSTON — Dozens of independent boards that regulate doctors, barbers, electrical workers and an array of other professionals could soon be pulled under the state’s umbrella — a move that trade groups complain smacks of government overreach.
Lawmakers are considering a bill filed by Gov. Charlie Baker to limit the independence of licensing boards and give the state the power to “review and veto” any action deemed to stifle competition.
The proposal responds to a U.S. Supreme Court opinion last year that boards controlled by members of the profession they regulate are not immune from antitrust lawsuits.
In that case, the court ruled that the state dental board in North Carolina had no protection from antitrust claims when it issued cease-and-desist orders to companies offering teeth-whitening services.
Baker administration officials say the ruling leaves licensing boards in Massachusetts vulnerable.
Even legal actions may be challenged, Mike Kaneb, Baker’s deputy legal counsel, told a legislative committee on Tuesday.
“Individual board members can be sued,” he added.
But exerting authority over the boards is also raising concerns.
Frank Callahan, president of the Massachusetts Building Trades Council, which represents about 75,000 skilled construction workers, said the state needs to address the issue but he’s concerned the governor’s proposal would give the state too much power over the boards.
Boards that oversee electricians and other skilled trades already have state oversight, to varying degrees, he noted, as well as lawyers to ensure their decisions comply with federal anti-trust laws.
Baker moves to control professional boards | News | eagletribune.com 13/5/16 11:14 PM
Several representatives of trade groups opposed the proposal at the legislative hearing. Robert Butler, business manager for Sheet Metal Workers Local 17, called it a “solution to a nonexistent problem.”
“This bill would allow the state to make decisions without any public input or recourse,” he said.
Baker, a Republican, has promised to make the state more business- friendly, in part by cutting through red tape. In a statement, he said licensing rules and limits on professionals “have the effect of restraining trade and commerce” and are bad for business.
Donna Kelly-Williams, president of the Massachusetts Nurse’s Association, criticized his plan in comments to lawmakers.
“With this directive, it seems as though the governor would like to turn the Board of Registered Nurses and other similar boards into nothing more than vehicles to spur economic competition at the expense of the public health and safety,” she said.
Baker administration officials said that’s not the intent.
“The only motivation for the governor’s bill is to respond to the changes in law,” Kaneb said Tuesday.
Since the Supreme Court ruling, legislation to exert more control over independent licensing boards has been introduced in least six other states, according to the National Conference on State Legislatures.
In Massachusetts, the Division of Professional Licensure oversees 45 boards, which regulate more than 370,000 individuals and businesses in some 50 trades and professions.
Most board members are volunteers appointed the governor and operate independently from the state.
Baker signed an executive order last year directing the licensing division and other agencies to conduct monthly reviews of recent board decisions to determine if any violate federal laws.
Martin W. Healy, chief counsel for the Massachusetts Bar Association, said the state must act quickly to comply with the Supreme Court ruling to ensure that its boards don’t face legal challenges.
Baker moves to control professional boards | News | eagletribune.com 13/5/16 11:14 PM
“This is a major issue for the state that needs to be addressed quickly,” he said. “You would have a very difficult time attracting talented people to these positions if they could held personally liable for the board’s decisions.”
Christian Wade covers the Massachusetts Statehouse for the North of Boston Media Group’s newspapers and websites.
MA – State Oversight of Professional Licensing Boards – annot

“The biggest problem Straight has is knowing how good it is.”–Dr. Robert Dupont, M.D., 1981
In 2012 former Nixon Drug Czar Robert Dupont, MD delivered the keynote speech at the Drug and Alcohol Testing Industry Association annual conference and described a “new paradigm” for addiction and substance abuse treatment. He advocated zero tolerance for alcohol and drug use that is enforced by monitoring with frequent random drug and alcohol tests. Detection of any substances is met with swift and certain consequences. He proposed expansion of this paradigm to other populations including workplace, healthcare, and schools.
Robert Dupont was a key figure in launching the “war on drugs” which is now widely viewed as a failure that has turned the US into the largest jailer in the world.
As the founding director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), he administered a 1.8 million dollar grant in 1972 to an experimental…
View original post 322 more words
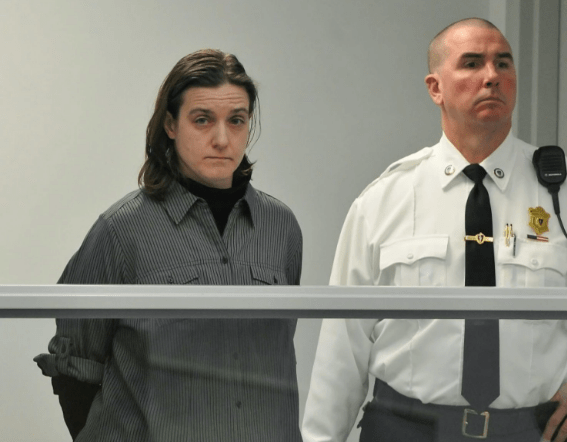

A knowing smile must have come across Sonja Farak’s face if she ever read the above quote from Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas during her nearly eight-years as a chemist for the Massachusetts crime lab. The list of illicit pharmaceuticals found in the trunk of Dr. Gonzo’s red Chevrolet convertible was not unlike her very own workstation stash in terms of diversity and color. Farak’s personal bindle, however, just happened to reside within the walls of the Amherst facility where she worked as a chemist analyzing seized substances brought in by police and the buffet of illicit pharmaceuticals and industrial quantities Farak snorted, smoked and swallowed while testing drugs for criminal cases is jaw dropping.
Referring to his own drug use, Charlie Sheen once said …”I probably took more than anybody could survive,” during an ABC interview. “I was banging seven-gram rocks. Because that’s how I roll. I have one speed. I have one gear.” Sheen noted his most recent binge was “radical. … The run I was on made Sinatra, Flynn, Jagger, Richards look like droopy-eyed, armless children.” But Farak’s run would make even the most hardcore drug user stand up and take notice as this woman was not just under the influence but over the rainbow and her eclectic pharmacopeia and hepatic fortitude alone is breathtaking but the kicker is this–she did it all within the walls of the state run crime lab and no one noticed.
Farak’s drug use started in 2004 when she started sampling from the “primary standards” that chemists use as a reference to compare to the the seized samples brought in by police. “Primary samples” are of very high quality and the Amherst lab maintained samples of everything from heroin to marijuana. Farak developed a penchant for Meth and by 2005 had increased her usage to multiple times per day. By 2009 she had nearly exhausted the labs entire methamphetamine supply.
Farak told investigators that she smoked crack every day at work. When police in Chicopee, Mass. seized a kilo of cocaine, Farak utilized that lab facilities to freebase about 100 grams of it and free is a very good price. When it struck her fancy she also took methamphetamine, amphetamine, ketamine, ecstasy LSD, Marijuana and MDMA at work and at home. She also testified in court while drug addled and even hit the crack pipe prior to a 2012 state police accreditation inspection of the lab. Farak remained undetected amongst those trained to detect. Throughout her entire binge, no one noticed a decline in her work, with one colleague even calling her “meticulous” and “dedicated to her work.”
Farak was arrested in 2013 after it was inexplicably discovered that her lab samples that she had been tampering with for nearly eight-years had been tampered with. Chunks of crack were found at her work station and a crack pipe in her car.
She pleaded guilty in January 2014 to tampering with a handful of drug samples and served an 18-month sentence. She was prosecuted and the Massachusetts attorney general’s office said at the time they did “not believe Farak’s alleged tampering would undermine any cases” but three years later, an investigation by Attorney General Maura Healey reveals otherwise.
Farak’s pursuit to oblivion rivals that of Permanent Midnight, Jerry Stahl’s autobiographical account his prodigious drug use as he wrote television shows but the potential consequences of Farak’s diehard addiction and penchant for psychotropics are more than just shabby dialogue on Moonlighting or Alf. Losses of liberties and freedoms can result from positive drug tests and the consequences can be grave and far reaching. Positive drug tests can tear apart families end careers and trigger suicides.
A spokeswoman for Attorney General Maura Healey said the information gathered about Farak “will no doubt have implications for many cases.” One defense attorney told the Boston Herald that Farak handled about 30,000 cases over the course of her career.
Some defense attorneys maintain that prosecutorial misconduct kept the details of Farak’s drug-induced work secret for almost two years after her problems were discovered.
Cyndi Ray Gonzalez, chief spokeswoman for Massachusetts Attorney General Maura Healey, said that the state’s district attorneys, the defense bar and the courts “are going to have to collectively work on determining the universe of cases that could be affected. And they’re going to have to determine how best to notify the people in each case.”
Matthew Segal of the American Civil Liberties Union of Massachusetts has been fighting Massachusetts prosecutors for almost four years to learn the names of all those affected by Dookhan’s misconduct. “This is why it’s not just about two chemists, it’s about an entire system that allowed this to happen, and once it did happen didn’t take steps to remedy it.”
The newly released investigation was prompted by a ruling from the state Supreme Judicial Court last April, which said top state law enforcement officials failed to fully investigate how many times Farak tampered with drug evidence after her arrest in 2013. “This is a statewide problem,” said attorney Luke Ryan, who helped bring the scope of Farak’s drug use and evidence tampering to light, and who represents several defendants whose samples purportedly were tested by Farak. “The fact that we’re doing this in 2016 instead of 2013 makes the job so much harder. . . . The chances of people falling through the cracks really increases.” According to spokesman Jake Wark state’s district attorneys are undertaking research similar to that performed in the wake of the Dookhan scandal
“Our experience with the Hinton Lab crisis has provided us with a framework for identifying and acting on these cases,” Wark said, referring to ex-chemist Annie Dookhan, who was found to have been falsifying her analysis reports to police and the courts for years and potentially tainting up to 40,000 cases. Identifying and acting? How about preventing?
Farak and Dookhan’s misdeeds were initially dismissed as a minor issue by government lawyers. -These egregious debacles are not just a matter of “bad apples” but a complete organizational systems failure in a culture of deference with no internal controls and an absence of outside accountability. In both cases the blinkered apathy is glaringly obvious and some people felt it was easier not to examine or look too deeply into the matter.

The photo above was taken at the 104th Annual Meeting of the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB) held in San Diego April 28-30 and tweeted last night in reference to the partnership between the FSMB and the Federation of State Physician Health Programs (FSPHP) with the caption:
“How a healing profession heals itself #FSMB2016 partnerships #FSPHP trust and faith in oversight and system.”
Within the the allotted 140 character twitter limit this succinct observation is nevertheless very revelatory. Both systems and the oversight of systems demand accountability and answerability to outside and independent agencies. Trust and Faith are not in the equation. Why has this lesson not been learned?
Answerability requires the obligation to answer questions regarding decisions and actions. Accountability requires transparency, explanation and justification. What was done and why? Standards, rules, regulations, codes, laws and other objective benchmarks need to be applied by outside actors. This is critical. It is the very essence of oversight.
“Trust and faith in oversight and system” is both oxymoronic and nonsensical. “Faith and trust” in oversight equates with an “absence” of oversight. “Faith and trust” in systems inevitably results in “systems failure” and therein lies the problem.
Blind faith and deference to authority has led to a systems failure in the regulation of the medical profession. Physician health programs (PHP’s) have convinced state medical boards to give them complete deference. Medical board’s in turn have convinced state attorney generals and law enforcement to give them complete deference. This has led to a complete systems failure. No investigatory or oversight body exists. No one is minding the minders. It is a complete and utter free for all.
Making sound decisions about regulation calls for an understanding of the problem it is intended to solve. Legitimate policy must be based on recognized institutions and experts. Regulatory changes demand methodologically sound science and evidence-based facts arrived at through rigorous peer review and professional oversight. The science must be reliable and unbiased. Legitimate policy must be based on recognized institutions and experts. If the information regulatory agencies rely on to discipline doctors and protect the public is unreliable then serious consequences can occur.
The validity and reliability of opinions lie in their underlying methodology and evidence base. Reliance on the personal authority of any expert or group of experts is the fallacy of appeal to authority and a more apt and accurate twitter caption to the photo above would be Algernon Sidney’s 1683 statement that:
“Implicit Faith belongs to Fools, and Truth is comprehended by examining Principles”
They can be a terror to your mind and show you how to hold your tongue
They got mystery written all over their forehead
They kill babies in the crib and say only the good die young
They don’t believe in mercy
Judgement on them is something that you’ll never see
They can exalt you up or bring you down main route
Turn you into anything that they want you to be–Bob Dylan, Foot of Pride
Although no reliable statistics yet exist, anecdotal reports suggest a marked rise in physician suicide in recent years. From the reports I am receiving it is a lot more than the oft cited “medical school class” of 400 per year.
This necessitates an evaluation of predisposing risk factors such as substance abuse and depression, but also requires a critical examination of what external forces may be involved in the descent from suicidal ideation to suicidal planning to completed suicide. What are the cumulative situational and psychosocial factors in physicians that make suicide a potential option and what acute events precipitate the final act?
Depression and Substance Abuse no Different from General Population
The prevalence of depression in physicians is close to that of the general population 1,2 and, if one looks critically at the evidence based literature, substance abuse in medical professionals approximates that of the general population. Controlled studies using DSM diagnostic criteria indicate that physicians have the same rates (8-14%) of substance abuse and dependence as the general population,3 and slightly lower rates compared to other occupations.4,5 Epidemiological surveys reveal the same. Hughes, et al.6 reported a lifetime prevalence of drug or alcohol abuse or dependence in physicians of 7.9%, markedly less than the 14.6% prevalence reported in the general population by Kessler.7
Job Stress and Untreated Mental Illness Risk Factors
Job stress coupled with inadequate treatment for mental illness may be factors contributing to physician suicide according to one recent study. Using data from the National Violent Death Reporting System, Gold, Sen, & Schwenk, 2013 8 compared 203 physicians who had committed suicide to more than 31,000 non-physicians and found that having a known mental health disorder or a job problem that contributed to the suicide significantly predicted being a physician. Physicians were 3.12 times more likely to have a job problem as a contributing factor. In addition, toxicology testing showed low rates of medication treatment. The authors concluded that inadequate treatment and increased problems related to job stress are potentially modifiable risk factors to reduce suicidal death among physicians. They also warned that the database used likely underestimated physician suicides because of “underreporting and even deliberate miscoding because of the stigma attached.”8
Few studies have evaluated the psychosocial stressors surrounding physician suicide but there is no reason to believe they are any different from the rest of the population. Although the triggering life events and specific stressors may vary outside, the inner psyche and undercurrent of thoughts and feelings should remains the same. Perhaps the same drivers of suicide identified in other populations are contributing to physician suicide.
Perceived Helplessness, Hopelessness, Bullying and Defeat
Perceived helplessness is significantly associated with suicide as is9 Hopelessness10,11 Bullying is known to be a predominant trigger for adolescent suicide12-14 One study found that adolescents in custody who were bullied were 9.22 times more likely to attempt suicide than those were not bullied.15
Heightened perceptions of defeat and entrapment are known to be powerful contributors to suicide.16,17 The “Cry of Pain” model 18,19 specifies that people are particularly prone to suicide when life experiences are interpreted as signaling defeat which is defined as a sense of “failed struggle” or loss of social position and resources.. The person is unable to identify an escape from or resolution to a defeating situation, a sense of entrapment proliferates with the perception of no way out, and this provides the central impetus for ending ones life. There is a helplessness and hopelessness that precipitates the descent from ideation, to planning, and then to finality.
Organizational Justice Important Protective Factor
In a study on Italian and Swedish female physicians, degrading experiences and harassment at work were found to be the most powerful independent variables contributing to suicidal thoughts.20 Degrading work experiences harassment, and lack of control over working conditions were found to be associated with suicidal thoughts among Italian and Swedish male university physicians.21
Evidence exists for the role of rescue factors (i.e. social support) as buffers against suicide in the face of varying degrees of life stress.22,23 The study of female physicians revealed meetings to discuss stressful work experiences as a potential protective factor, 20 and support at work when difficulties arose appeared to be a protective factor for the male physicians.21 In line with this, studies of Finnish physicians found that control over one’s work and organizational justice were the most important determinants of work-related wellbeing.24,25 Organizational justice has been identified as a psychosocial predictor of health and wellbeing26 27 Low organizational justice has been identified as a notable risk factor for psychological distress and depression.28,29
Historical Precedent-the Suicides at Ridgeview
Could these factors be playing a role in physician suicide? They evidently did at the Ridgeview Institute, a drug and alcohol treatment program for impaired physicians in Metropolitan Atlanta created by G. Douglas Talbott. Talbott helped organize and served as past president of the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) and was a formative figure in the American Medical Association’s (AMA’s) Impaired Physician Program. He has owned and directed a number of treatment facilities for impaired professionals, most recently the Talbott Recovery Campus in Atlanta, one of the preferred referrals for physicians ordered into evaluation and treatment by licensing boards.
After creating the DeKalb County Impaired Physicians Committee for the Medical Association of Georgia, Talbott founded the Georgia Disabled Doctors Program in 1975 in part because “traditional one-month treatment programs are inadequate for disabled doctors.” According to Talbott, rehabilitation programs that evaluate and treat the rest of the population for substance abuse issues are incapable of doing so in doctors as they are unlike others. He bases this uniqueness on “incredibly high denial”, and what he calls the “four MDs,” “M-Deity”, “Massive Denial” “Militant Defensiveness”, and “More Drugs.”30
Contingency Management = Extortion Using Medical License
According to Talbott, “impaired doctors must first acknowledge their addiction and overcome their ‘terminal uniqueness’ before they can deal with a drug or alcohol problem.” “Terminal uniqueness “ is a phrase Talbott uses to describe doctors’ tendency to think they can heal themselves. “M-Deity” refers to doctors “being trained to think they’re God,”31 an unfounded generalization considering the vast diversity of individuals that make up our profession. This attitude, according to some critics, stems from the personal histories of the treatment staff, including Talbott, who are recovering alcoholics and addicts themselves. One such critic was Assistant Surgeon General under C. Everett Koop John C. Duffy who said that Ridgeview suffered from a “boot-camp mentality” toward physicians under their care and “assume every physician suffering from substance abuse is the same lying, stealing, cheating, manipulating individual they were when they had the illness. Certainly some physicians are manipulative, but it’s naïve to label all physicians with these problems.”32
American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) President (1981-1983) LeClair Bissell was also highly critical of Talbott’s approach. Bissell, co-author of the first textbook of ethics for addiction professionals33 when asked if there was any justification to the claim that doctors are sicker than other people and more vulnerable to addiction replied:
“Well, based on my treatment experience, I think they are less sick and much easier to treat than many other groups. I think one reason for that is that in order to become a physician…one has to have jumped over a great many hurdles. One must pass the exams, survive the screening tests and the interviews, be able to organize oneself well enough to do examinations and so on, and be observed by a good many colleagues along the way. Therefore I think the more grossly psychotic, or sicker, are frequently screened out along the way. The ones we get in treatment are usually people who are less brain-damaged, are still quite capable of learning, are reasonably bright. Not only that, but they are quite well motivated in most cases to hang on to their licenses, the threat of the loss of which is frequently what puts them in treatment in the first place. So are they hard to treat? No! Are they easy patients? Yes! Are they more likely to be addicted than other groups? We don’t know.”34
“I’m not much for the bullying that goes along with some of these programs,” Bissell commented to the Atlanta Journal and Constitution in 1987.31 The constitution did a series of reports after five inpatients committed suicide during a four-year period at Ridgeview.35 In addition there were at least 20 more who had killed themselves over the preceding 12 years after leaving the treatment center.32
Bissell, the recipient of the 1997 Elizabeth Blackwell Award for outstanding contributions to the cause of women and medicine remarked: “When you’ve got them by the license, that’s pretty strong leverage. You shouldn’t have to pound on them so much. You could be asking for trouble.”31According to Bissell: “There’s a lot of debate in the field over whether treatment imposed by threats is worthwhile…To a large degree a person has to seek the treatment on his own accord before it will work for him.”31
A jury awarded $1.3 million to the widow of one of the deceased physicians against Ridgeview,36 and other lawsuits initiated on behalf of suicides were settled out of court.35
The Constitution reported that doctors entered the program under threats of loss of licensure “even when they would prefer treatment that is cheaper and closer to home.” 37 The paper also noted that Ridgeview “enjoys unparalleled connections with many local and state medical societies that work with troubled doctors,” “licensing boards often seek recommendations from such groups in devising an approved treatment plan,” and those in charge are often “physicians who themselves have successfully completed Ridgeview’s program.”37
The cost of a 28-day program for nonprofessionals at Ridgeview in 1987 was $10,000 while the cost was “higher for those going through impaired-health professionals program,” which lasted months rather than 28 days.32
In 1997 William L. White interviewed Bissell whom he called “one of the pioneers in the treatment of impaired professionals.” The interview was not published until after hear death in 2008 per her request. Noting her book Alcoholism in the Professions38 “remains one of the classics in the field”, White asked her when those in the field began to see physicians and other professionals as a special treatment population. She replied:
“When they started making money in alcoholism. As soon as insurance started covering treatment, suddenly you heard that residential treatment was necessary for almost everybody. And since alcoholic docs had tons of money compared to the rest of the public, they not only needed residential treatment, they needed residential treatment in a special treatment facility for many months as opposed to the shorter periods of time that other people needed.”39
Talbott claimed a “92.3 percent recovery rate, according to information compiled from a five-year follow-up survey based on complete abstinence and other treatment.”40
“There is nothing special about a doctor’s alcoholism,” said Bissel
“these special facilities will tell you that they come up with really wonderful recovery rates. They do. And the reason they do is that any time you can grab a professional person by the license and compel him or her into treatment and force them to cooperate with that treatment and then monitor them for years, you’ll get good outcomes—in the high 80s or low 90s in recovery rates—no matter what else you do.”39
“The ones I think are really the best ones were not specialized. There were other well-known specialty clinics that claimed all the docs they treated got well, which is sheer rot. They harmed a great many people, keeping them for long, unnecessary treatments and seeing to it that they hit their financial bottom for sure: kids being yanked out of college, being forced to sell homes to pay for treatment, and otherwise being blackmailed on the grounds that your husband has a fatal disease. It’s ugly.”39
Stanton Peele’s “In the Belly of the American Society of Addiction Medicine Beast” describes the coercion, bullying, threats and indoctrination that are standard operating procedure in Talbott’s facilities.41 Uncooperative patients, “and this covers a range of sins of commission or omission including offering one’s opinion about one’s treatment,” are “threatened with expulsion and with not being certified-or advocated for with their Boards.”41 The cornerstone of treatment is 12-step spiritual recovery. All new patients are indoctrinated into A.A. and coerced to confess they are addicts or alcoholics. Failure to participate in A.A. and 12-step spirituality means expulsion from the program with the anticipated result being loss of one’s medical license.
Fraud, Malpractice, False Diagnoses and False imprisonment
In May 1999 Talbott stepped down as president of the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) as a jury awarded Dr. Leonard Masters a judgment of $1.3 million in actual damages and an undisclosed sum in punitive damages for fraud, malpractice, and the novel claim of false imprisonment.42 The fraud finding required a finding that errors in the diagnosis were intentional. After being accused of excessive prescribing of narcotics to his chronic pain patients, Masters was told by the director of the Florida PHP that he could either surrender his medical license until the allegations were disproved or submit to a four-day evaluation. Masters agreed to the latter, thinking he would have an objective and fair evaluation, but was instead diagnosed as “alcohol dependent” and coerced into the Talbott recovery program. He was forced to stay in the program under threat of his medical license as staff would routinely threaten to report any doctor who questioned any aspect of their diagnosis or treatment to their state medical boards “as being an impaired physician, leaving necessary treatment against medical advice”42 which would mean the loss of his licensure. However, Masters was not an alcoholic. According to his attorney, Eric. S. Block, “No one ever accused him of having a problem with alcohol. Not his friends, not his wife, not his seven children, not his fellow doctors, not his employees, not his employers, No one.” 43 He was released 4 months later and forced to sign a five-year “continuing care” contract with the PHP, also under continued threat of his medical license. Talbott faced no professional repercussions and no changes in the treatment protocols were made. Talbott continued to present himself and ASAM as the most qualified advocate for the assessment and treatment of medical professionals for substance abuse and addiction up until his death last year.44
Same System Imposed on Doctors Today—Institutional Injustice Worse due to Laboratory Developed Tests. Fortified Scaffold and Tightened the Noose.
In almost all states today any physician referred for an assessment for substance abuse will be mandated to do so in a facility just like Ridgeview. There is no choice. There is one difference however. When the Ridgeview suicides occurred the plethora of laboratory developed tests were not yet introduced. A decade ago Dr. Gregory Skipper introduced the first laboratory developed test for forensic testing and used it on doctors in physician health programs. These non-FDA approved tests of unknown validity presented a new unpredictable variable into the mix with a positive test necessitating another assessment at an out of state treatment facility—a “PHP-approved” assessment facility. The addition of this laboratory Russian Roulette renders the current system much worse than it was at the time of the Ridgeview suicides.
And if a positive test occurs there are no safeguards protecting the donor. LDTs are unregulated by the FDA. There is no oversight and no one to file a complaint with.
In addition the PHPs have no oversight by the medical boards, departments of health or medical societies. They police themselves. The PHPs have convinced law enforcement that when it comes to doctors it is a “parochial issue” best handled by the medical community. I have been hearing from doctors all over the country who have tried to report crimes to the local police, the state Attorney General and other law enforcement agencies only to be turned back over to the very perpetrators of the crimes. “He’s a sick doctor, we’ll take care of him.” The “swift and certain consequences” of this are an effective means of keeping the rest of the inmates silent. Likewise doctors have been going to the media only to have the door slammed in their faces because the media has generally bought in to the “impaired” and “disruptive” physician construct these same people developed through propaganda, misinformation and moral panics and crusades.
Urgent Need to Admit to the Problem
There has been an increase in physician suicide in the past decade. By my estimate the numbers are going to be far higher than the oft-cited 400 per year. The speculation as to cause has been unenlightening and in fact frustrating. Knowledge of anatomy, access to dangerous drugs, increased workload and even student loans have been proposed as contributing factors. Although there has been some tangential mention of physician health programs it has been indirect. Direct and defined discussion is necessary and state PHPs need to be named as a possible contributor to suicide. Admitting the possibility there is a problem is the first crucial step in defining and addressing the problem. The 1980s historical precedent is correlated with physician suicide. The current system is not only based on Ridgeview but has been fortified in scope and power. The physician health movement has effectively removed due process from doctors while removing answerability and accountability from themselves. And they have not only fortified the scaffold but widened it from substance abusing doctors to all doctors. “Potential impairment” and “relapse without use” were introduced without any meaningful resistance and they are now using a panoply of non-FDA approved laboratory developed tests of unknown validity to test for substances of abuse in a zero-tolerance abstinence based monitoring program. With no regulatory oversight the stage is set not only for error but misuse as witch-pricking devices for punishment and control. Doctors across the country are complaining of the very same abuses Leonard Masters did–false diagnoses, misdiagnosis, unneeded treatment and fraud.
In summary, any doctor who is referred to their state PHP today is required to have any assessment and treatment at a “PHP-approved” facility based on Ridgeview. It is mandated. There is no choice. Coercion, control and abuse at Ridgeview was associated with multiple suicides in doctors in the 1980s. The use of non-FDA approved tests of unknown validity worsens the abuse and fits the “cry of pain” model of hopelessness, helplessness and despair. Locus of control is lost. Organizational justice is absent.
The temporal relationship is clear.
Why is this still the elephant in the room?
This needs to be named, defined and openly discussed and debated. How many more must die before we speak up?
Please help me get the conversation going.

“Conformity is the jailer of freedom and the enemy of growth.” – John F. Kennedy.
Born – May 29, 1917
Brookline, Massachusetts,
Died- November 22, 1963
Dallas, Texas, aged 46

 To evaluate the legitimacy of an authority it is necessary to:
To evaluate the legitimacy of an authority it is necessary to:
 The dogmatic statements and abusive generalizations do not conform to reality.
The dogmatic statements and abusive generalizations do not conform to reality.If one looks behind the curtain there is not much there. 
Historical, political, economic and social analysis can all show how the construct that exists today came to be. This can be factually ascertained by simple reasoning and examination of the documentary evidence.
Any one of these analyses would reveal that the “PHP-blueprint” is a false-construct built on circumnavigation and obfuscation.
An evidence-based scrutiny of the literature would reveal it to be invalid and of little probative value. A public policy analysis would reveal the logical fallacies involved in trumpeting their positions including exaggerated rhetoric and fear monitoring strategies designed to inspire moral panics and exploit fears to further an underlying political agenda
Any critical analysis would reveal cherry picking. proof by anecdote, deceptive propaganda, double talk, contradictory, illogical and incomprehensible jabber, unprovable and un-disprovable statements and a panoply of logical fallacy.
These groups misrepresent, censor and suppress. They nit pick and split hairs.  The concept of denial is not just used to force people into treatment and justify abuse during treatment but to suppress specific questions and deliberately avoid key facts.
The concept of denial is not just used to force people into treatment and justify abuse during treatment but to suppress specific questions and deliberately avoid key facts.
So why are we not questioning this “authority?” They have been left alone and basically thrown in the backyard left to proliferate like feral cats.

We need anti-authoritarians and we need them now.
I need allies before the door closes for good. And that door may be closing a lot sooner than you think!




Need allies and funding to continue the fight against institutional injustice in the medical profession and work towards physician (professional ) health reform.
Please help me work toward real change on disruptedphysician.com before it is too late.
To make a contribution please click here or visit gofundme website.