

Laboratory Developed Tests
Questions about the accuracy and marketing of Laboratory Developed Tests (LDTs) led to last years debate on whether or not the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) should regulate a subset of diagnostic tests currently exempted from oversight. Designed to bring clinical tests to market such as those for rare diseases that the costly FDA process would otherwise preclude, the LDT pathway bypasses Federal regulation and oversight. The LDT pathway additionally bypasses any semblance of accountability. It is an honor system and, as with any honor system, it is a system that can be exploited by the dishonorable.
Questions about the validity of these tests raised concerns over patient safety and this led to a call for oversight. Among those asking for regulation were Massachusetts Senators Edward J. Markey and Elizabeth Warren.
Opponents of regulation argued that the LDT pathway enables new and pioneering tests to be developed quickly and improve patient care. A viewpoint piece published in JAMA opposing regulation noted such advances have occurred “in large part because of the nimbleness of relatively small clinical and academic laboratories that can quickly respond to new medical findings and patient needs by rapidly and safely developing and improving laboratory-developed tests.”
But the LDT pathway does not require proof of test validity, that the test is actually testing for what it claims to be testing, and with no FDA oversight a lab can claim any validity it wants in marketing the test. There is no accountability. Proponents of regulation argue that this lack of oversight is a direct threat to patient safety and, as an opposing viewpoint piece in JAMA notes, a “patient’s life or death could hinge on whether a single, unregulated diagnostic test result is meaningful.”
The debate focused on the reliability and validity of a number of clinical tests currently marketed with unverified claims of accuracy such as those used for prenatal screening and Lyme disease. Notably absent from the discussions are the vast number of Laboratory Developed Tests tests being used for “forensic” drug and alcohol testing with the current FDA draft guidance stating simply:
“At this time, FDA will continue to defer oversight of the use of these tests in the forensics (law enforcement) setting to the existing system of legal controls, such as the rules of evidence in judicial proceedings and other protections afforded through the judicial process.”
The debate focused on the unreliability of lab tests such as those for Lyme disease but simply glossed over forensic drug and alcohol tests. Let’s think about this critically for a moment as a false positive test for Lyme disease can result in unneeded treatment and costs but a false drug or alcohol test can result in consequences far more grave such as loss of a child, loss of a professional license, and imprisonment. The results of a positive forensic test for drugs can be far reaching and permanent. So how did this happen?
The answer is simple. Money and profit. Lobbying groups such as the Drug and Alcohol Testing Industry Association (DATIA) ( which represents more than 1,200 companies involved in the drug and alcohol testing industry simply said “How dare you interfere with our war on drugs?” and the tests were off the table. The DATIA even employs its own DC based lobbying firm, Washington Policy Associates, and money talks. How dare anyone interfere with the profiteering ambitions to utilize junk-science in the mainstream population as specifically and explicitly spelled out in Robert Dupont’s 2012 keynote speech before the Drug and Alcohol Testing Industry Association and in the American Society of Addiction Medicine’s (ASAM’s ) White Paper on Drug Testing. These two documents should be required reading for anyone interested in civil liberties and fundamental freedoms. That they have been disregarded by most is incomprehensible and worthy of exploration. These documents both propose random mandatory and unnecessary and insurance paid drug-testing utilizing the medical profession (pediatricians to obstetricians to geriatricians) as a drug-testing collection agency using not only urine samples but also blood , oral fluid (saliva), hair, nails, sweat and breath.” It is all spelled out concisely-just read the papers.

The Birth of EtG: The Introduction and Marketing of Laboratory Developed Tests for “Forensic” Drug Testing Via a Lucrative Loophole
Numerous “forensic” tests of unknown validity using urine, blood, hair, fingernails breath and saliva have been developed and brought to market as LDTs since the first one was introduced in 2003 when ASAM physician Dr. Gregory Skipper, then Medical Director of the Alabama Physicians Health Program, “convinced the initial lab in the USA, NMS near Philadelphia to start performing EtG testing.”1 With essentially no evidence base Skipper then claimed the alcohol biomarker “appeared to be 100 percent specific” in detecting covert use of alcohol for several days after ingestion based on a study he coauthored that involved a mere 35 forensic psychiatric inpatients in Germany, all male2
 Using an arbitrary cutoff level of 100 ug/L the EtG was marketed as a valid and reliable test and blindly tested on those being monitored by programs not beholden to the strict protocol and procedure dictated by the Mandatory Guidelines for Federal Workplace Drug Testing that most Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) adopted. In other words, the test was used on those who possessed little power or had their power removed.
Using an arbitrary cutoff level of 100 ug/L the EtG was marketed as a valid and reliable test and blindly tested on those being monitored by programs not beholden to the strict protocol and procedure dictated by the Mandatory Guidelines for Federal Workplace Drug Testing that most Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) adopted. In other words, the test was used on those who possessed little power or had their power removed.
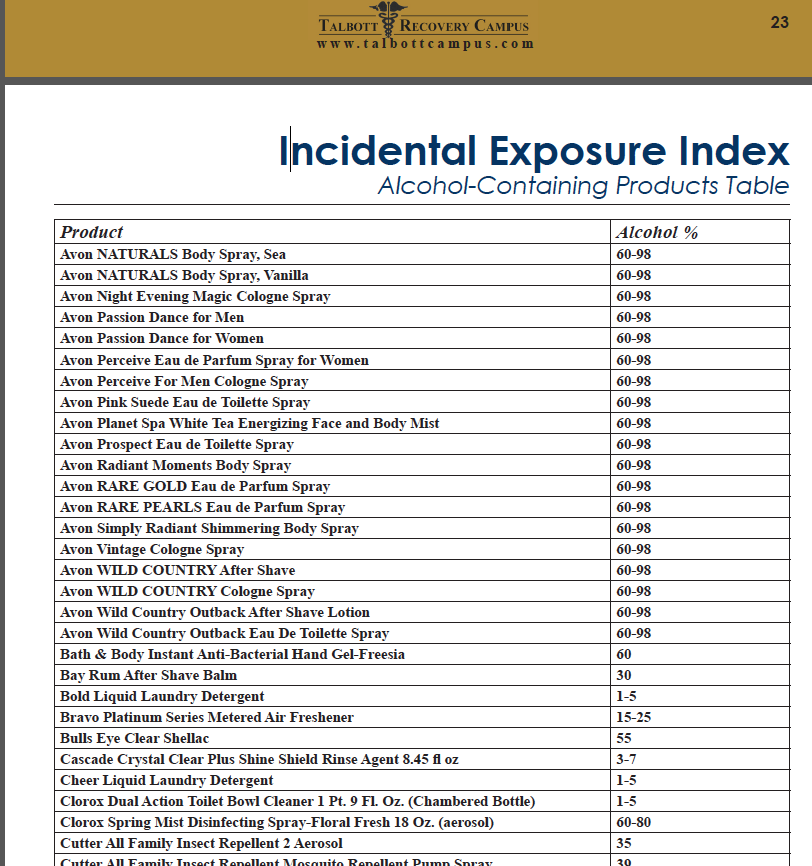
The test was subsequently found to be so sensitive that it could measure incidental exposure to alcohol in foods, over the counter cold medications, mouthwash3,4, hand sanitizer gel5, and nonalcoholic wine.6 Sauerkraut and bananas have even been shown to cause positive levels.7

Shortly after the EtG debuted, complaints began to accumulate from individuals testing positive who adamantly proclaimed they did not drink. Steadfast in their trust of expert opinion and the claimed accuracy of EtG, the complaints of the accused were largely disregarded by those doing the monitoring. People lost their licenses, jobs, careers, and reputations. Others lost their freedom or had their children taken away. It is unknown how many died by suicide.
There have been multiple lawsuits filed since the introduction of the EtG including a class-action suit, but these were inevitably met with a well-funded and deep legal defense and their “experts.” The labs have taken a “stand your ground” position yielding either dismissals or in favor of the defense. As a new to the market lab with no prior evidence-based research in forensic testing prior to its implementation and use for forensic testing, the proponents of EtG testing had no meaningful opposition in terms of a scientific body of facts and evidence and no credible voice to present it. With the only “experts” in EtG validity being those who introduced and promoted its use there were no counter-forces. Those suffering the consequences of a false-positive test had no recourse. But as the toll of mayhem increased it eventually reached a tipping-point where others began to take notice.
In 2006 the Wall Street Journal reported the problems with the EtG to the general public,8 and SAMHSA issued an advisory stating that “legal or disciplinary action based solely on a positive EtG…. is inappropriate and scientifically unsupportable at this time. These tests should currently be considered as potential valuable clinical tools, but their use in forensic settings is premature.”9
Since that time Skipper has served as expert witness in close to 46 administrative hearings 22 criminal 14 custody and 1 Federal class action suit.

But this did not stop the Federation of State Physician Health Programs from using the EtG on physicians being monitored. Instead they instructed doctors to avoid anything potentially containing alcohol including hand sanitizer which a 2011 study found could result in EtG concentrations of almost 2000 ug/L. 10 To continue to justify the use of EtG they added other LDTs as confirmation tests of LDTs such as EtS and PEth– Junk Science to confirm junk science. Nonsensical smoke-and-mirrors antithetical to science and evidence-based medicine.
Since the birth of the EtG a variety of tests have been introduced and marketed as LDTs utilizing nails, blood, hair, breath and urine—all with unknown validity but marketed without constraint. No regulation, oversight or accountability exists.
The newest gadget they are using on doctors is the Cellular Digital Photo Breathalyze which he is promoting in the same manner as the EtG after a study he co-authored with Robert Dupont on just 12 subjects.
Expanding Laboratory Developed Tests to Test Everyone: The ASAM White Paper on Drug-Testing and the “New Paradigm”
Although the current use of these tests is limited to the criminal justice system and professional monitoring programs this may soon change as the American Society of Addiction Medicine is proposing a “new paradigm” of zero-tolerance random widespread drug and alcohol testing. This is outlined in the ASAM White Paper on Drug Testing and described by Robert Dupont in his keynote speech before the Drug and Alcohol Testing Industry Association (DATIA) annual conference in 2012.
The ASAM White paper states drug testing is “vastly underutilized” throughout healthcare and describes the use of drug testing “within the practice of medicine and, beyond that, broadly within American Society.”
As the consequences of a single unregulated “forensic” test result can be grave, far-reaching and even permanent it is critical that these tests be included in the debate on regulation of LDTs.
Evidence based medicine is not restricted to randomized trials and meta-analyses. It involves tracking down the best external evidence with which to answer our clinical questions.11
Expert opinion is the lowest level of evidence available in the EBM paradigm.12,13 Fortunately, the scientific method and Cochrane type critical analysis of the available evidence is a tool to help people progress toward the truth despite their susceptibilities to unconscious confirmatory bias or conscious confirmatory distortion .14 Unfortunately, no one has used these tools address they panoply of tests of unknown validity that have already entered the market ; poised to be used on virtually everyone.
It has now been 18 months since my Open Letter to Elizabeth Warren and the response thus far has been silence. Not a word since then.
- Skipper G. Exploring the Reliability, Frequency, and Methods of Drug Testing: What is Enough to Ensure Compliance?: Alcohol Markers and Devices. 2013; http://www.fsphp.org/Skipper, Exploring the Reliability Frequency and Methods 2 Presentation.pdf.
- Wurst FM, Vogel R, Jachau K, et al. Ethyl glucuronide discloses recent covert alcohol use not detected by standard testing in forensic psychiatric inpatients. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. Mar 2003;27(3):471-476.
- Costantino A, Digregorio EJ, Korn W, Spayd S, Rieders F. The effect of the use of mouthwash on ethylglucuronide concentrations in urine. Journal of analytical toxicology. Nov-Dec 2006;30(9):659-662.
- Reisfield GM, Goldberger BA, Pesce AJ, et al. Ethyl glucuronide, ethyl sulfate, and ethanol in urine after intensive exposure to high ethanol content mouthwash. Journal of analytical toxicology. Jun 2011;35(5):264-268.
- Rosano TG, Lin J. Ethyl glucuronide excretion in humans following oral administration of and dermal exposure to ethanol. Journal of analytical toxicology. Oct 2008;32(8):594-600.
- Hoiseth G, Yttredal B, Karinen R, Gjerde H, Christophersen A. Levels of ethyl glucuronide and ethyl sulfate in oral fluid, blood, and urine after use of mouthwash and ingestion of nonalcoholic wine. J Anal Toxicol. Mar 2010;34(2):84-88.
- Musshoff F, Albermann E, Madea B. Ethyl glucuronide and ethyl sulfate in urine after consumption of various beverages and foods–misleading results? Int J Legal Med. Nov 2010;124(6):623-630.
- Helliker K. A test for alcohol–and its flaws. The Wall Street Journal2006.
- Administration SAaMHS. The role of biomarkers in the treatment of alcohol use disorders. In: Advisory SAT, ed2006:1-7.
- Reisfield GM, Goldberger BA, Crews BO, et al. Ethyl glucuronide, ethyl sulfate, and ethanol in urine after sustained exposure to an ethanol-based hand sanitizer. Journal of analytical toxicology. Mar 2011;35(2):85-91.
- Sackett DL, Rosenberg WM, Gray JA, Haynes RB, Richardson WS. Evidence based medicine: what it is and what it isn’t. BMJ. Jan 13 1996;312(7023):71-72.
- Shaneyfelt TM, Centor RM. Reassessment of clinical practice guidelines: go gently into that good night. JAMA. Feb 25 2009;301(8):868-869.
- Straus SE, Green ML, Bell DS, et al. Evaluating the teaching of evidence based medicine: conceptual framework. BMJ. Oct 30 2004;329(7473):1029-1032.
- Haack S. Defending Science–Within Reason: Between Scientism and Cynicism. Amherst, N.Y.: Prometheus Books; 2003.





[…] Source: The Need for Regulatory Oversight of Laboratory Developed Tests (LDTs) in Drug and Alcohol Testing: … […]
LikeLike
Reblogged this on Disrupted Physician.
LikeLike